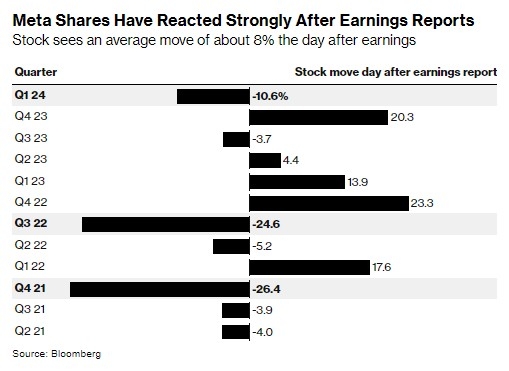
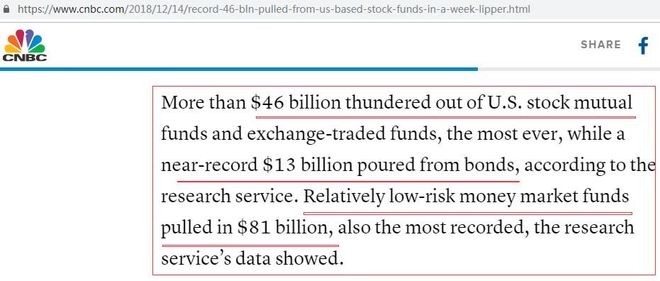
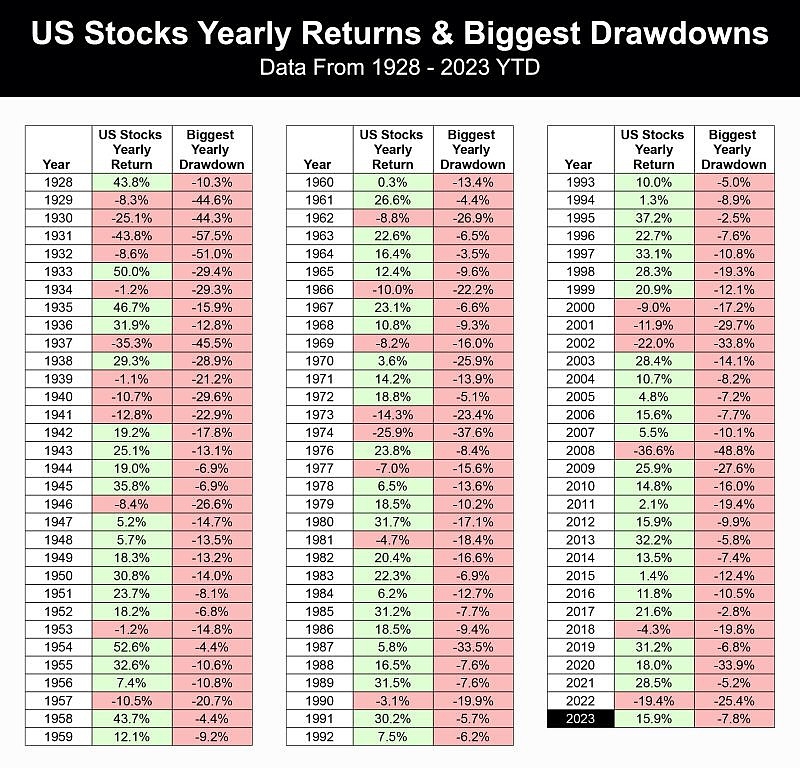
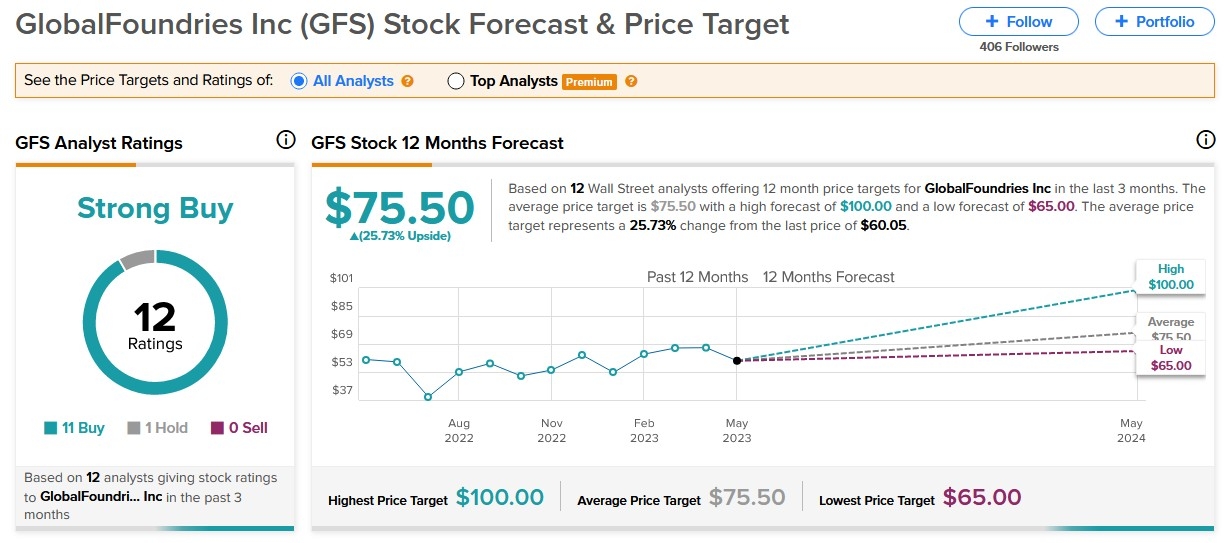
In the United States, investing in the stock market can be a lucrative venture. However, it's crucial to understand the tax implications of stock profits. This article delves into the details of how stock profits are taxed in the US, providing investors with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
Capital Gains Tax
When you sell stocks for a profit, the gains are subject to capital gains tax. The rate at which these gains are taxed depends on how long you held the stock before selling it.
Short-term Capital Gains: If you held the stock for less than a year, the gains are considered short-term and are taxed as ordinary income. This means they are subject to your regular income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%.
Long-term Capital Gains: If you held the stock for more than a year, the gains are considered long-term and are taxed at a lower rate. The rates for long-term capital gains are 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your taxable income.
Taxable Income and Bracket
Your taxable income determines the rate at which your long-term capital gains are taxed. Here's a breakdown of the rates:
- 0%: If your taxable income is below the threshold for your filing status, your long-term capital gains may be taxed at 0%.
- 15%: If your taxable income is between the thresholds for your filing status, your long-term capital gains will be taxed at 15%.
- 20%: If your taxable income exceeds the thresholds for your filing status, your long-term capital gains will be taxed at 20%.
Tax Reporting
When you sell stocks for a profit, you must report the transaction on your tax return. This is done using Form 8949 and Schedule D. These forms help you calculate your capital gains and losses, and determine the tax you owe.
Example
Let's say you bought 100 shares of a stock for
If your taxable income is below the threshold for your filing status, you would pay no tax on this gain. If your taxable income is between the thresholds, you would pay 15% tax on the gain. If your taxable income exceeds the thresholds, you would pay 20% tax on the gain.
Impact of Tax Planning
Understanding the tax on stock profit is essential for effective tax planning. Investors can minimize their tax liability by strategically timing their stock sales and considering factors such as holding periods and taxable income.
Conclusion
Taxing stock profits is a complex topic, but it's crucial for investors to understand the rules and implications. By knowing how your stock profits are taxed, you can make informed decisions and potentially minimize your tax liability. Always consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
Title: How the US Dollar Value Effects Stoc? America stock market