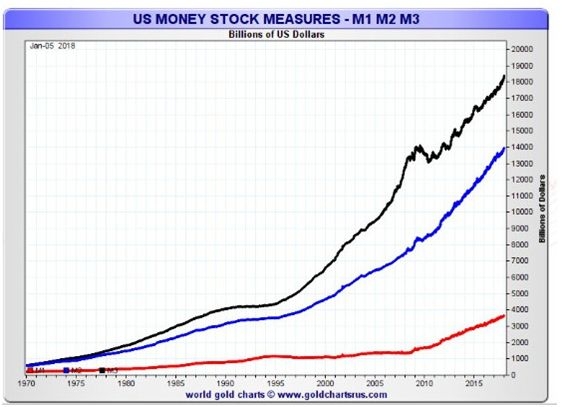
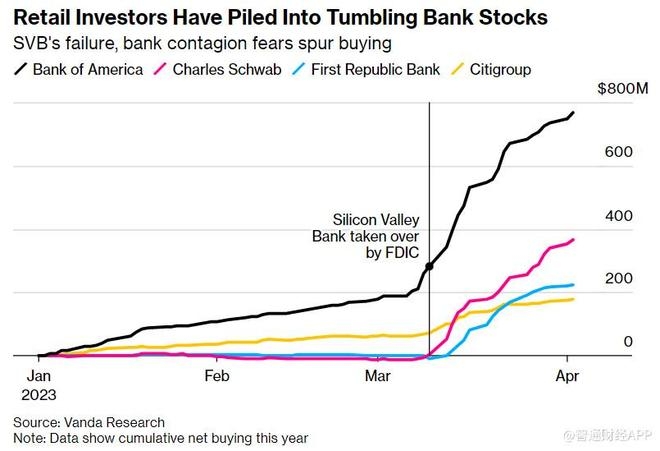
Are you an American investor with shares in US stocks? Are you worried about the implications of the Canada capital gains tax on your investments? You're not alone. Many American investors are curious about how Canadian tax laws affect their investments in US stocks. In this article, we delve into the details of the Canada capital gains tax on US stocks, helping you understand the implications and plan accordingly.
What is Capital Gains Tax?
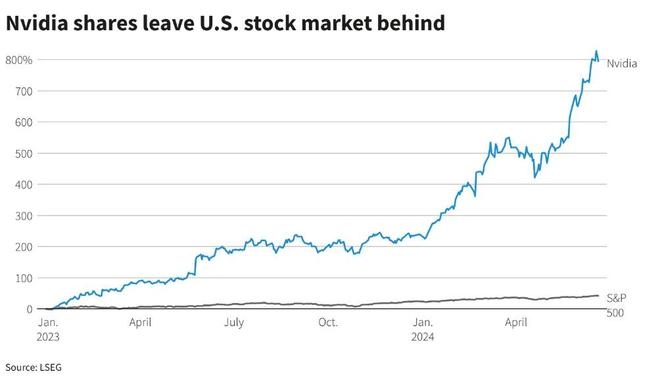
Firstly, it's essential to understand what capital gains tax is. Capital gains tax is a tax imposed on the profit you make from selling an asset, such as stocks, real estate, or other investments. In Canada, this tax is levied on the profit you make from selling stocks, including those from US companies.
How is Capital Gains Tax Calculated?
The Canada capital gains tax on US stocks is calculated by determining the capital gain, which is the difference between the selling price of the stock and its adjusted cost base. The adjusted cost base is essentially the amount you paid for the stock, including any additional costs like brokerage fees.
Once you've determined the capital gain, you multiply it by your marginal tax rate. In Canada, the marginal tax rate varies depending on your income level and province. For example, if you're in Ontario and your marginal tax rate is 40%, and you have a capital gain of
Deducting US Tax Paid
One crucial aspect to consider is that you may have already paid tax on the income from your US stocks in the United States. Under the Canada-US Tax Treaty, you can deduct the foreign tax paid from your Canadian tax liability. This means that you won't be taxed twice on the same income.
Reporting US Stocks in Canada
When you file your Canadian income tax return, you must report the sale of your US stocks. This is done through Schedule 3, Capital Gains (or Losses). Ensure that you have all the necessary information, such as the date of purchase, the cost of the shares, and the selling price.
Case Study: John's US Stock Sale
Let's take a hypothetical example. John bought 100 shares of a US company for
Conclusion
Understanding the Canada capital gains tax on US stocks is crucial for American investors. By knowing how this tax is calculated and the deductions available, you can plan your investments more effectively and minimize your tax liability. Always consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
Artius II Acquisition Inc. Rights: Pre-mark? Us stock information